Presentation Title
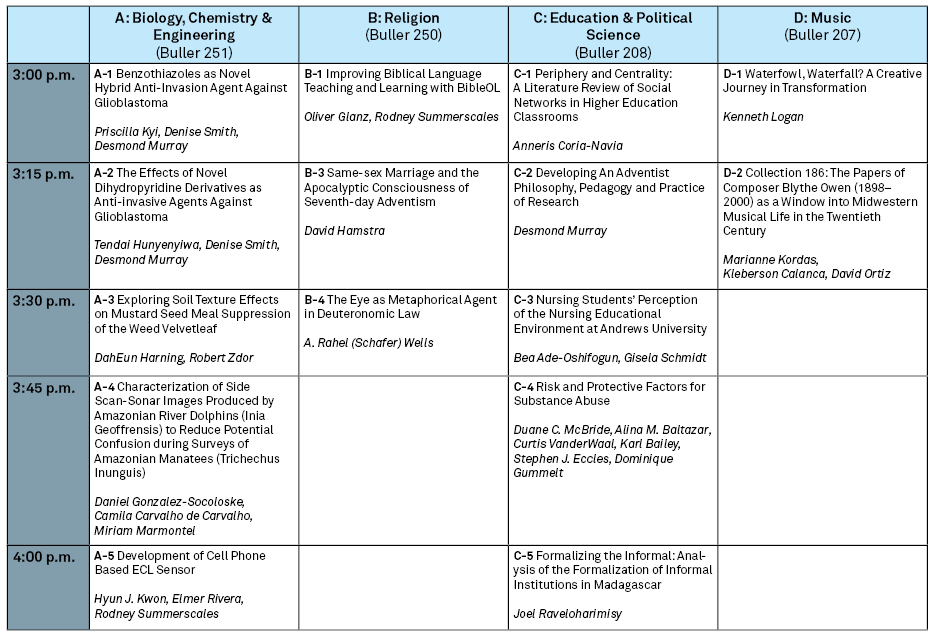
C-3 Nursing Students’ Perception of the Nursing Educational Environment at Andrews University
Presenter Status
Nursing Department Chair
Preferred Session
Oral Session
Start Date
26-10-2018 3:30 PM
End Date
26-10-2018 3:45 PM
Presentation Abstract
Aim:
The aim of this study is to describe how nursing students perceive their educational environment using the Dundee Ready Educational Environment Measure (DREEM) questionnaire.
Objectives:
The objectives of this study are to measure the nursing students’ perception of their educational environment; and compare nursing students’ perception of educational environment within cohorts (sophomore, junior and senior).
Background and Rationale:
The educational environment of a nursing schools have different determinants which can affect the way a student performs in the school and some of these determinants are captured in the Dundee Ready Education Environment Measure (DREEM) questionnaire (Roff 2005). The Nursing program at Andrews University went through decreasing enrollment. The university planned to make positive changes. A baseline measure will give reliable data to inform planned changes. The results gained from the present study could be used to implement changes in curricula and educational environment, which may therefore improve NCLEX passing rates, and improve the students’ perceptions of the nursing program.
Research Methodology:
This is a cross sectional research study utilizing a convenience sample of all students enrolled in the nursing program during Fall 2015 semester. DREEM questionnaire was utilized with permission from the author. Hard copies were given to students with implied consent on the front page. Completed copies submitted anonymously via sealed envelopes. The study received approval from Andrews University IRB. Total DREEM scores were compared across cohorts and subscale (domain) data analyzed using ANOVA (SPSS) to determine any significance (p = 0.05). DREEM is a quantitative assessment of five domains: Perceptions of Learning (PL); Perceptions of Teaching (PT); Academic Self –Perceptions (ASP); Perceptions of Atmosphere (PA); and Social Self-Perceptions (SSP).
Results:
A total of 39 students were surveyed. 16 sophomores, 8 juniors and 15 seniors. Total DREEM scores showed 20% of the senior students perceiving their educational environment as having lots of problems and it filtered through all the DREEM domains. For example, comparisons of scores revealed that the senior students significantly scored their social self-perception lower than the sophomores, F (2, 36) = 3.912, p =.03. Though not significant, 20% of seniors also perceived their academic atmosphere as having many issues. The perception of teaching was good across all cohorts with no significant difference. The students see the teachers as model teachers. 20% of the senior students have more negative perception of their learning while other cohorts had positive perceptions. Though there is no significant difference between cohorts, 31% of sophomores had a negative academic self-perception. In general, most students perceive their educational environment as positive. The senior cohort stands out in their negative perceptions of Andrews University’s educational environment.
Conclusion:
This study highlights the need to focus on the senior year of the nursing program. A detailed analysis of the experience of the senior year will help to reveal the factors causing dissatisfaction with the seniors especially in their social life. This is more important because students prepare for the NCLEX-RN and exit examinations during their senior year.
C-3 Nursing Students’ Perception of the Nursing Educational Environment at Andrews University
Aim:
The aim of this study is to describe how nursing students perceive their educational environment using the Dundee Ready Educational Environment Measure (DREEM) questionnaire.
Objectives:
The objectives of this study are to measure the nursing students’ perception of their educational environment; and compare nursing students’ perception of educational environment within cohorts (sophomore, junior and senior).
Background and Rationale:
The educational environment of a nursing schools have different determinants which can affect the way a student performs in the school and some of these determinants are captured in the Dundee Ready Education Environment Measure (DREEM) questionnaire (Roff 2005). The Nursing program at Andrews University went through decreasing enrollment. The university planned to make positive changes. A baseline measure will give reliable data to inform planned changes. The results gained from the present study could be used to implement changes in curricula and educational environment, which may therefore improve NCLEX passing rates, and improve the students’ perceptions of the nursing program.
Research Methodology:
This is a cross sectional research study utilizing a convenience sample of all students enrolled in the nursing program during Fall 2015 semester. DREEM questionnaire was utilized with permission from the author. Hard copies were given to students with implied consent on the front page. Completed copies submitted anonymously via sealed envelopes. The study received approval from Andrews University IRB. Total DREEM scores were compared across cohorts and subscale (domain) data analyzed using ANOVA (SPSS) to determine any significance (p = 0.05). DREEM is a quantitative assessment of five domains: Perceptions of Learning (PL); Perceptions of Teaching (PT); Academic Self –Perceptions (ASP); Perceptions of Atmosphere (PA); and Social Self-Perceptions (SSP).
Results:
A total of 39 students were surveyed. 16 sophomores, 8 juniors and 15 seniors. Total DREEM scores showed 20% of the senior students perceiving their educational environment as having lots of problems and it filtered through all the DREEM domains. For example, comparisons of scores revealed that the senior students significantly scored their social self-perception lower than the sophomores, F (2, 36) = 3.912, p =.03. Though not significant, 20% of seniors also perceived their academic atmosphere as having many issues. The perception of teaching was good across all cohorts with no significant difference. The students see the teachers as model teachers. 20% of the senior students have more negative perception of their learning while other cohorts had positive perceptions. Though there is no significant difference between cohorts, 31% of sophomores had a negative academic self-perception. In general, most students perceive their educational environment as positive. The senior cohort stands out in their negative perceptions of Andrews University’s educational environment.
Conclusion:
This study highlights the need to focus on the senior year of the nursing program. A detailed analysis of the experience of the senior year will help to reveal the factors causing dissatisfaction with the seniors especially in their social life. This is more important because students prepare for the NCLEX-RN and exit examinations during their senior year.



Acknowledgments
Nursing Students at Andrews University for completing the survey questions.