Oral Breakout Sessions
Presentation Title
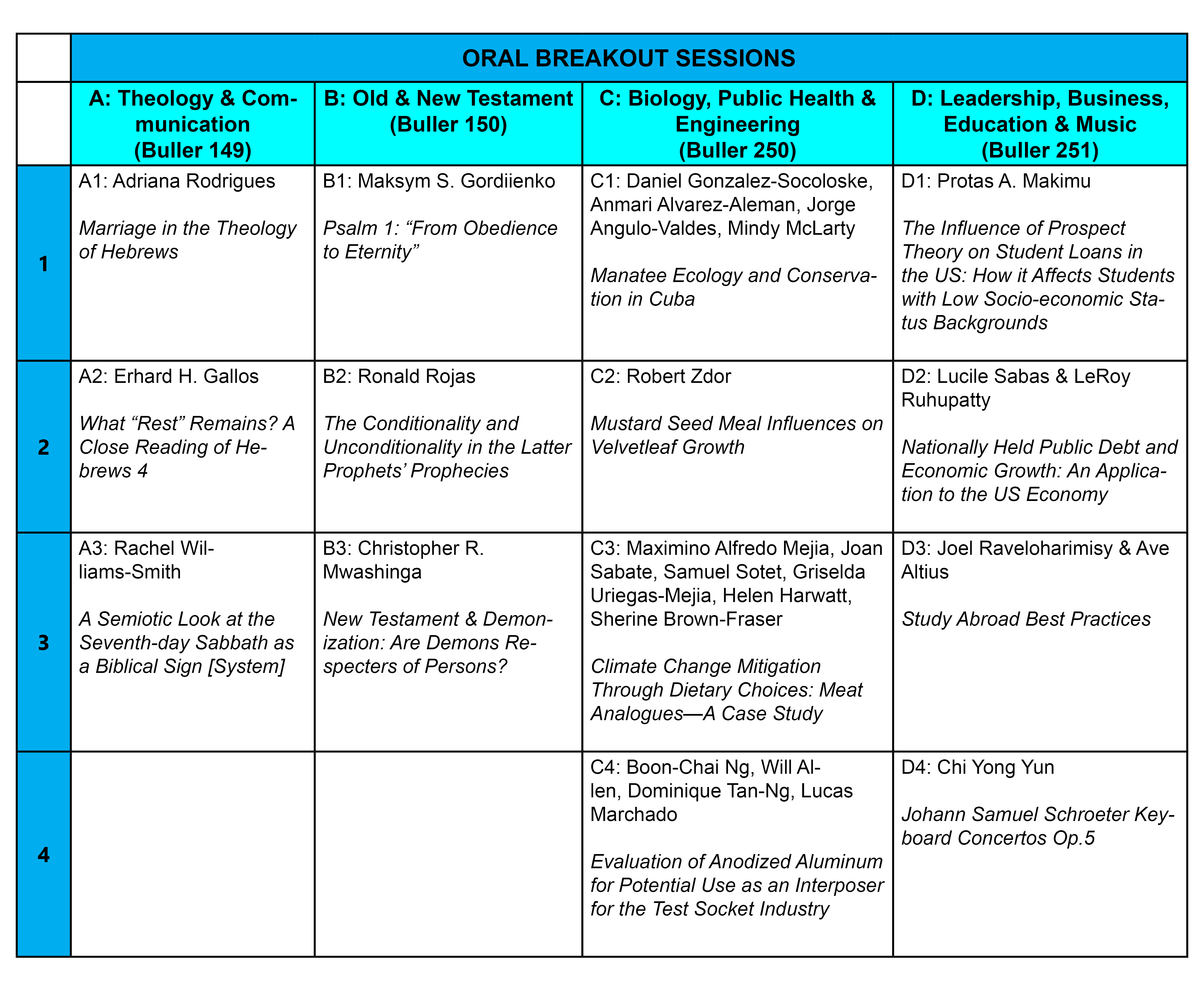
D-1 The Influence of Prospect Theory on Student Loans in the US: How it Affects Students with Low Socio-economic Status Backgrounds
Presenter Status
Graduate Student, Department of Leadership
Preferred Session
Oral Session
Start Date
30-10-2015 3:00 PM
End Date
30-10-2015 3:15 PM
Presentation Abstract
Prospect theory is a behavioral theory, which is employed to determine how people make choices between different options or prospects. It describes, explains, and predicts the choices that an individual makes, especially in situations when the outcomes are uncertain.
It is used to explain a common pattern of choice, and is descriptive and empirical in nature. It involves two parts of decision making: the editing, or framing, and evaluation phases. The editing deals with framing effects while the evaluation involves the decision process of choosing among options. The decision is influenced by two processes: one related to subjective value and the second related to perceptual likelihood.
Framing is controlled by the manner in which a choice problem is presented as well as the norms, habits, and expectancies of the decision maker.
The evaluation phase consists of two parts: the value function and weight function. The value function has three components. The first one is denoted in terms of gains and losses relative to the reference point, the second one is that the value function is convex below the reference point and concave above it, and the third one is the asymmetric nature of the value; it is steeper in the domain of losses than gains. This means that losing hurts more than comparable gain pleases.
This study reveals how American students from low socio-economic backgrounds have disadvantages in making choices on the issue of student loans for financing higher education with respect to prospect theory.
D-1 The Influence of Prospect Theory on Student Loans in the US: How it Affects Students with Low Socio-economic Status Backgrounds
Prospect theory is a behavioral theory, which is employed to determine how people make choices between different options or prospects. It describes, explains, and predicts the choices that an individual makes, especially in situations when the outcomes are uncertain.
It is used to explain a common pattern of choice, and is descriptive and empirical in nature. It involves two parts of decision making: the editing, or framing, and evaluation phases. The editing deals with framing effects while the evaluation involves the decision process of choosing among options. The decision is influenced by two processes: one related to subjective value and the second related to perceptual likelihood.
Framing is controlled by the manner in which a choice problem is presented as well as the norms, habits, and expectancies of the decision maker.
The evaluation phase consists of two parts: the value function and weight function. The value function has three components. The first one is denoted in terms of gains and losses relative to the reference point, the second one is that the value function is convex below the reference point and concave above it, and the third one is the asymmetric nature of the value; it is steeper in the domain of losses than gains. This means that losing hurts more than comparable gain pleases.
This study reveals how American students from low socio-economic backgrounds have disadvantages in making choices on the issue of student loans for financing higher education with respect to prospect theory.


